Consecutive Chain Min-Max Reduction
In Consecutive Sudoku if a cell has two consecutive peers, then that cell can't have the minimum and maximum values of possibilities that are available in those three cells.
An illustration for the above concept.
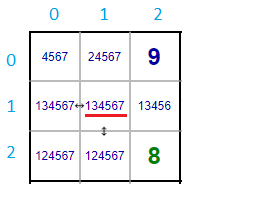
Here, we consider an example of rectangular block in Consecutive Sudoku. In this the cell (1,1) has two consective peer cells (1,0) and (2,1). The combination of all possibilities that are available in those three cells are {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}. Minimum and Maximum values among those possibilities are 1 and 7.
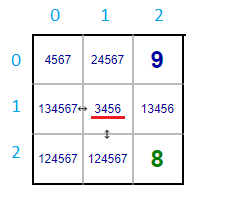
The cells (1,0) and (2,1) doesn't have consecutive value which is lesser than 1, therefore the minimum value 1 is removed from the cell (1,1). Likewise, in cells (1,0) and (2,1) no consecutive value greater than 7 is possible.Hence the values 7 is removed from the cell (1,1).
Algorithm Links
Consecutive Sudoku Algorithms
Greater Sudoku Algorithms



